We all know that cough is the most common illness that can occur. However, when there is a persistent cough that lasts longer than usual, then it will become the main symptoms of bronchitis. Normally, when people talk about bronchitis, they usually refer it as an acute bronchitis. And of course, the cough associated with acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses.
To begin with, acute bronchitis from medical viewpoint is a clinical diagnosis characterized by cough due to acute inflammation of the trachea and bronchi. When there is a swelling irritation of the bronchi (the large tubes that carry air to the lungs), this is when the bronchitis starts to develop. Acute bronchitis often occurs with a viral infection, such as the common cold and is sometimes known as a “chest cold”. Due to the fact that acute bronchitis is characterized by an acute onset of a persistent cough with or without sputum production, this particular disease ranks among the top 10 most common outpatient illnesses in the United States; affecting approximately 5% of adults annually and about 6% of children at least have one episode a year.
Basically, there are different types of bronchitis with different causes, symptoms and treatments. The two main types of bronchitis are called acute (short-term) and chronic (ongoing). Acute bronchitis, firstly, is a respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and swelling of the bronchi (breathing tubes) leading to increased mucus production. It is a short-term condition that usually resolves on its own within a few days or weeks where the lung function returns to normal. Secondly, chronic bronchitis is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the bronchi – the kind of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) condition where the cough persists at least 3 months or more; possibly occurring with a span of 2 years, which is more serious than the acute type.
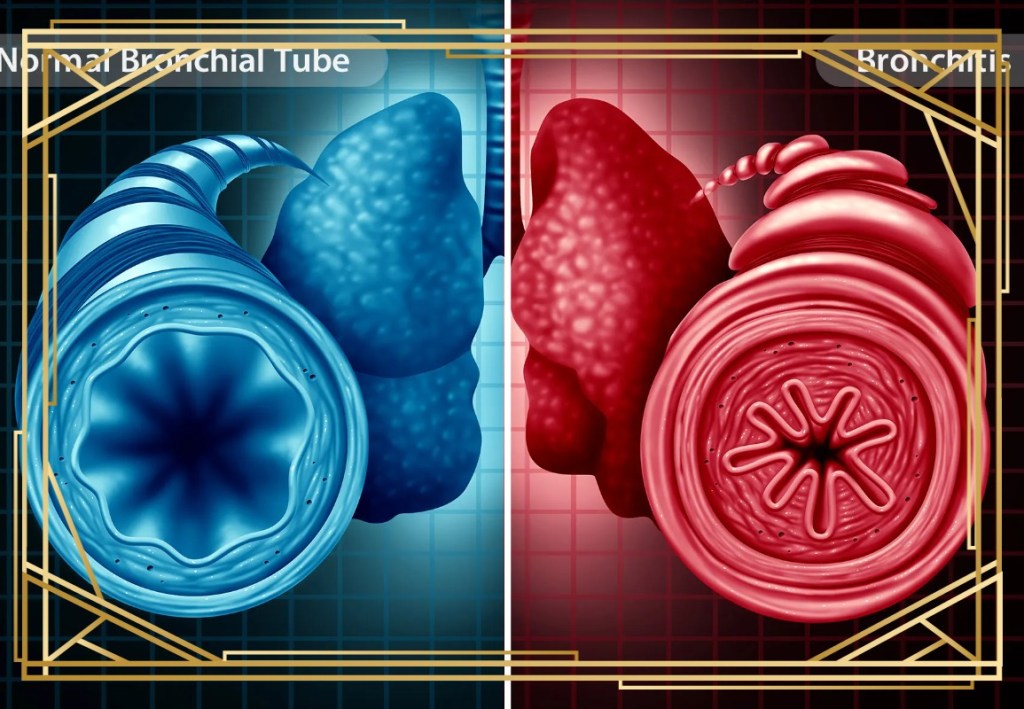
As mentioned previously, bronchitis happens when the bronchial tubes which carry air to the lungs become inflamed and swollen; causing a nagging cough and mucus. When you breathe, the air makes its way to your bronchial tubes, which are in the lungs. Bronchitis at this stage causes inflammation of these tubes (see the image below).

Generally, such infections or lung irritants cause acute bronchitis. The same viruses that cause colds and the flu are the most common cause of acute bronchitis. These viruses, additionally, are spread through the air when people cough. They also are spread through physical contact, for example, on hands that have not been washed. While acute bronchitis may last from a few days to several weeks, chronic bronchitis on the contrary may last up to months or even years. Therefore, if the lining of the bronchial tubes is constantly irritated and inflamed in the case of chronic bronchitis, it will result a patient to have a long-term cough with mucus where the symptoms can get much worse than usual.

You must be logged in to post a comment.